Blog
What is important to take into account in a Rotor Dynamics solution?
Rotor dynamics focuses on the study of the dynamics of rotating machines. Rotating machines are used in many sectors of the industry. Do these machines look similar? Yes!
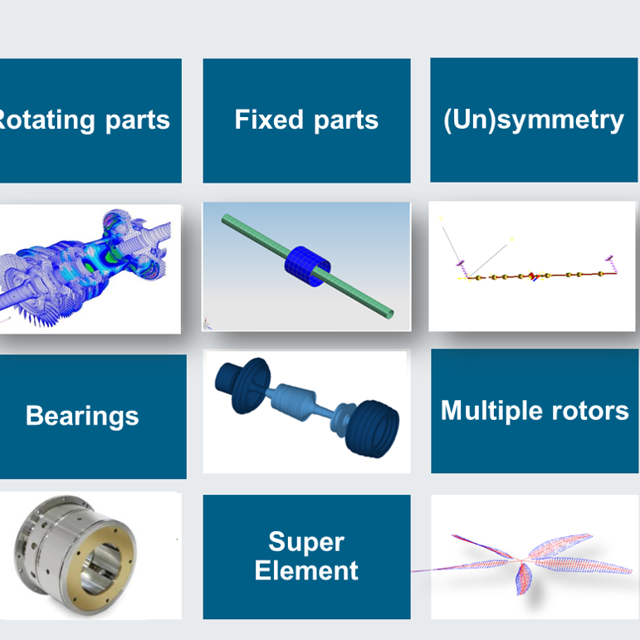
Those rotating machines are made of rotating parts, of fixed parts, and of linking devices. They are submitted to loads. Vibrations resulting from the rotation must be controlled to avoid the failure of parts of the whole system.
Rotor Dynamics analyses:
- are performed from the very beginning of the design cycle to prevent potential rotor dynamics instability problems,
- need non-linear analyses to take local effects into account,
- are used for correlation with testing.
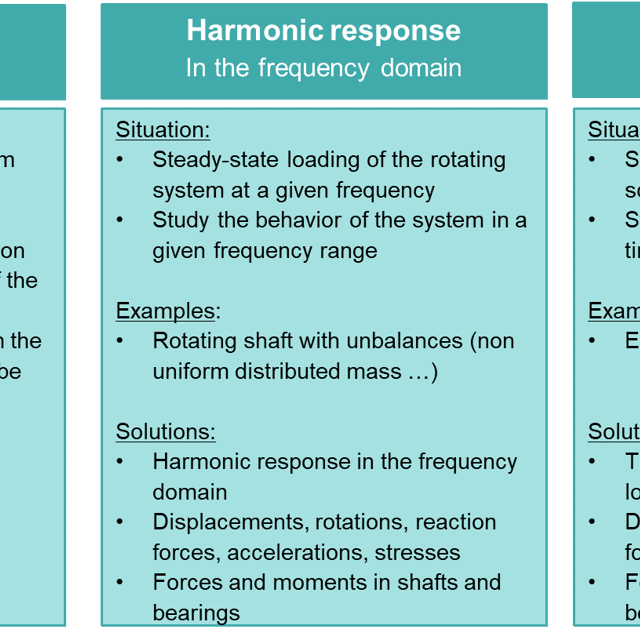
One of the main ébjectives of rotor dynamics is to identify the critical speed of the system. The critical rotational speed lead to large vibration amplitudes of the system and can cause damage or even failure of the system.
The other challanges with rotating machines are:
- impact of unbalanced loads,
- description of local stresses that could induce fatigue,
- description of bearings behavior, because bearing can influence a lot the behavior of the system.
WHAT is important to take into account in a Rotor Dynamics solution?
1) GYROSCOPIC EFFECT
When the shaft or bearings are deformed, it can induce a modification of the orientation of the axis of rotation. Gyroscopic effect is significant for high rotation speed and high polar moment of inertia.
2) WHIRL MODES
The whirling motion of the rotor can be in the same direction as the shaft's rotation (forward whirl) or in the opposite direction (backward whirl).
3) CORIOLIS EFFECT
When the rotating reference system is used, the Coriolis effect must be taken into account. When Newton's laws are transformed to a rotating frame of reference, the Coriolis force appear.
4) DAMPING
Damping can be represented as proportional damping, viscous (constant or variable) dambing, or hysterical damping.
5) MULTI-ROTORS
Multiple rotors, rotating at different speeds, can be managed in the same analysis. They can be modeled using a mixed representation.
6) MISALIGNMENT
The misalignement causes radial rotating displacements, and may lead to contact between the rotor and the stator.
7) STRESS AND STRAIN
High local stress could induce fatigue.